Aloe Vera and Its Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Imagine a plant so powerful that it can soothe burns, heal wounds, and even combat inflammation.
This isn’t a tale from ancient folklore; it’s the magic of Aloe vera.
This unassuming plant has been a staple in traditional medicine for centuries, and modern science is just catching up.
Today, we will look at its anti-inflammatory properties and discover why Aloe Vera is more than just a remedy for sunburns.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Aloe vera are attributed to various compounds, including chlorogenic acid, pyrocatechol, catechin, naringenin, rutin, quercetin, and cinnamic acid. Source.
Introducing Aloe Vera
Aloe vera, with its rich history rooted in ancient medicinal practices, has been cherished as a ‘miracle plant’ by many cultures around the world.
Hailing from the sunny landscapes of North Africa, this versatile plant has been a trusted companion for ailments ranging from skin irritations to digestive discomforts.
Central to its myriad of benefits are its potent anti-inflammatory qualities.
Let’s shed some light on its natural ability to combat inflammation and its enduring significance in today’s health landscape.
Aloe: the Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Aloe vera is a natural powerhouse when it comes to anti-inflammatory properties.
Various studies*, some even highlighted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), have confirmed that Aloe vera is rich in elements like special enzymes and beneficial vitamins. These components team up to provide relief from inflammation, making it especially helpful for conditions affecting the skin and digestive system.
Simply put, Aloe vera acts like a natural balm, calming down irritated areas and promoting healing.
Below, we will look into Aloe vera’s science-backed anti-inflammatory properties so you can clearly understand its benefits and how it can be a natural remedy in our daily lives.
*Links to some of the studies: this journal, this journal, this review, this journal.
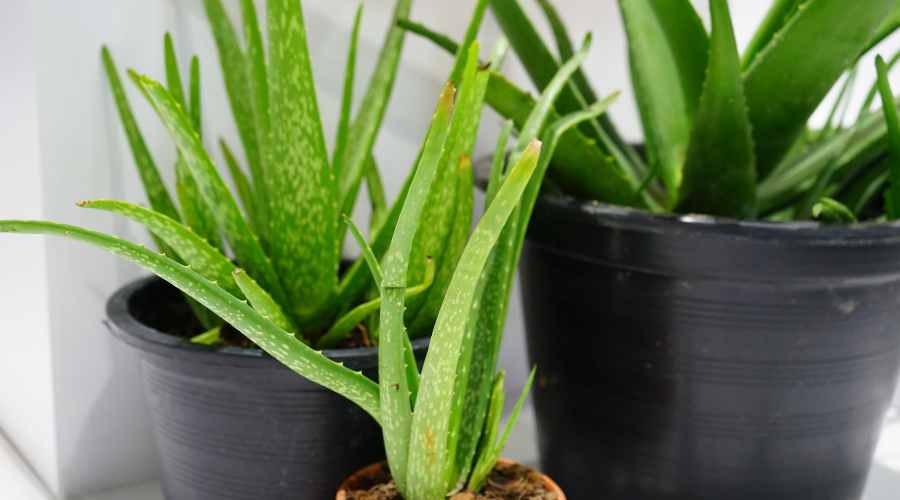

A Botanical Description
Aloe vera stands out with its tall, spear-like green leaves filled with a gooey gel.
These unique leaves are the plant’s treasure trove, packed with all its health wonders.
If you’ve ever travelled to sun-soaked destinations like the Canary Islands, India, or certain African spots, chances are you’ve come across this sun-loving plant.
Originally from the warm climes of North Africa, Aloe vera has since found its way to many sunny corners around the globe, gracing gardens and windowsills alike.
Chemical Constituents of Aloe Vera
Aloe vera isn’t just a pretty plant; it’s packed with a cocktail of natural goodies.
You’ll discover a treasure trove of nature’s finest elements in the Aloe vera leaf. A blend of essential vitamins, helpful enzymes, vital minerals, and special amino acids lies within its green confines.
One of its key ingredients are “polysaccharides,” which are known for their ability to calm and soothe the skin.
These ingredients and a few others are the secret behind Aloe vera’s renowned healing and soothing prowess.
Research from sources like the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) vouches for these benefits, showcasing the plant’s natural magic.

Mechanism of Anti-inflammatory Action
Here’s how Aloe vera works its anti-inflammatory magic: inflammation can be likened to a small fire at the cellular level, and Aloe vera acts as a soothing agent to quell it.
One way it achieves this is by neutralising ‘reactive oxygen metabolites’. These compounds, akin to tiny sparks, can exacerbate inflammation. Research from the Journal of Ethnopharmacology supports the idea that Aloe vera extracts can combat these reactive species.
Then we have ‘eicosanoids’ and ‘cytokines’. These are like the body’s internal communication system; when they get overly active, they can amplify inflammation.
Aloe vera can modulate the activity of these messengers, helping to reduce inflammation.
In a nutshell, it is clear that Aloe vera possesses a unique ability to maintain cellular harmony, ensuring our cells remain in a state of well-being.
Aloe Vera in Wound Healing
For many, Aloe vera is the go-to remedy for skin problems, but what’s the scientific verdict? A detailed systematic review explored the impact of Aloe vera on various skin injuries. The consensus? Aloe vera not only hastens the recovery time but also alleviates wound discomfort and size.
So, how does its knack for reducing inflammation fit into this? When our skin gets injured, inflammation is the body’s immediate reaction. It’s crucial for the healing journey, but too much of it can be counterproductive. Aloe acts as a balancer, ensuring inflammation is in check.
Regarding the kinds of skin issues Aloe vera can tackle, it’s a broad spectrum. Aloe vera has demonstrated its healing touch, from daily burns in the kitchen to surgical recovery, sun-induced redness, and even persistent skin conditions like psoriasis or bedsores.
In short, think of Aloe vera as nature’s healing balm, always on standby to mend and rejuvenate.
Aloe Vera’s Influence on Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Aloe vera has piqued the interest of researchers in relation to IBD.
A study titled “Anti-inflammatory effects of aloe vera gel in human colorectal mucosa in vitro” offers insights into this area. While the specific details of this research remain elusive at this moment, other scholarly works have underscored the beneficial role of Aloe vera in promoting gut health.
Certain compounds from the Aloe vera plant can help calm the inflammation within the digestive system. This provides a respite from the discomforts of IBD and nurtures a balanced gut environment.
Given its inherent properties to counter inflammation, Aloe vera stands out as a promising natural avenue for those navigating the challenges of gut inflammation.
Remember to consult your healthcare specialist before embracing Aloe vera or similar natural solutions.
Aloe Vera in the Beauty World
A comprehensive review titled “Evidence based medical use of aloe vera extracts, short review of literature” discusses the many uses of aloe vera, including its role in cosmetology (beauty).
The study highlights that while aloe vera is promoted for a vast array of conditions, its clinical effectiveness, especially in skincare, isn’t sufficiently defined yet. However, anecdotal evidence and traditional practices vouch for its soothing and moisturising properties.
One of the standout features of aloe vera gel is its ability to reduce skin inflammation. Inflammation can lead to various skin issues like redness, swelling, and itchiness.
Aloe vera, with its cooling and anti-inflammatory properties, can help alleviate these symptoms, making it a go-to remedy for sunburns, minor cuts, and other skin irritations.
Always remember, while aloe vera is generally safe for topical use, it’s essential to do a patch test before applying it extensively, especially for those with sensitive skin.

General Health Benefits and Immune System Enhancement
While I couldn’t directly access the study “Aloe vera: Potential candidate in health management via modulation of biological activities,” its title suggests a deep dive into the plant’s broader health impacts.
One of the standout benefits of aloe vera is its potential to bolster our immune system. (The immune system acts as our body’s defence mechanism, warding off illnesses and infections). Aloe vera appears to support and enhance this system, ensuring it functions optimally.
Additionally, aloe vera regulates various biological activities, ensuring our body’s processes are balanced and effective.
While topical aloe vera is renowned for skin relief, consuming it in various forms might offer a holistic boost to our health.
Applications and Uses of Aloe Vera for its Anti-inflammatory Properties
Skincare Products
One of Aloe vera’s standout features in skincare is its anti-inflammatory action. This makes it a prime ingredient in products designed to soothe irritated skin, reduce redness, and combat conditions like acne or rosacea. Its cooling effect is especially sought after in after-sun products to calm sunburned skin.
Therapeutic Uses
The anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera aren’t just skin-deep. It’s been considered for internal issues like inflammatory bowel diseases, where it may help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Additionally, when applied topically, it can aid in healing minor wounds by reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair.
Dietary Supplement
Consuming aloe vera, whether in juice form or as capsules, is believed to offer systemic anti-inflammatory benefits. This can be especially beneficial for individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions, helping to manage inflammation from within.
Safety and Precautions
Aloe vera, while beneficial, comes with its set of cautions:
Potential Side Effects
Consuming aloe vera, especially in large amounts, can lead to digestive issues like cramps or diarrhoea. Some might also experience allergic reactions when applying it topically.
Recommendations for Safe Usage
Always start with small amounts, whether applying it on the skin or ingesting it. For those considering aloe vera supplements, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare professional first.
Conclusion
Aloe vera stands out for its impressive anti-inflammatory prowess, making it a valuable asset in skincare and therapeutic applications.
While its benefits are promising, a world of potential is still waiting to be explored through further research.
It must be used with knowledge and caution as with any natural remedy.
References
- Surjushe A, Vasani R, Saple DG. Aloe vera: A short review. Indian J Dermatol. 2008;53(4):163-166. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2763764/
- Hekmatpou D, Mehrabi F, Rahzani K, Aminiyan A. The Effect of Aloe Vera Clinical Trials on Prevention and Healing of Skin Wound: A Systematic Review. Iran J Med Sci. 2019;44(1):1-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6330525/
- Langmead L, Feakins RM, Goldthorpe S, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral aloe vera gel for active ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;19(7):739-747. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01902.x
- Radha MH, Laxmipriya NP. Evaluation of biological properties and clinical effectiveness of Aloe vera: A systematic review. J Tradit Complement Med. 2015;5(1):21-26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4488101/
- Foster M, Hunter D, Samman S. Evaluation of the Nutritional and Metabolic Effects of Aloe vera. In: Benzie IFF, Wachtel-Galor S, editors. Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects. 2nd edition. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92765/
- Huseini HF, Kianbakht S, Hajiaghaee R, Dabaghian FH. Anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hypercholesterolemic effects of Aloe vera leaf gel in hyperlipidemic type 2 diabetic patients: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Planta Med. 2012;78(4):311-316. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22338121k
- Choonhakarn C, Busaracome P, Sripanidkulchai B, Sarakarn P. The efficacy of aloe vera gel in the treatment of oral lichen planus: a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158(3):573-577. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08370.x
- Vogler BK, Ernst E. Aloe vera: a systematic review of its clinical effectiveness. Br J Gen Pract. 1999;49(447):823-828. https://bjgp.org/content/49/447/823
