What is the Difference Between Acne and Pimples?
What is the difference between acne and pimples? Acne is a skin condition, while pimples are a symptom of it. Having pimples doesn’t always mean you have acne-prone skin. Acne is a skin issue with various blemishes, like blackheads and cysts. Factors like hormones and bacteria cause it. On the other hand, pimples are just one type of blemish.
While people with acne often get pimples, having a few pimples now and then doesn’t mean you have acne. It’s like a fever is a symptom of many illnesses, but not every fever means you have the flu.
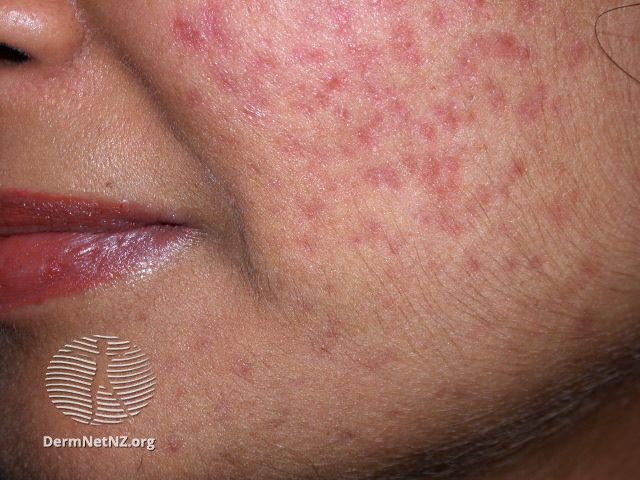
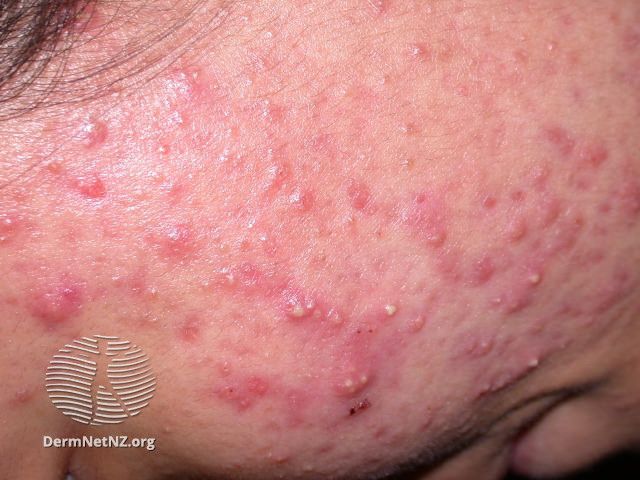
The Difference Between Acne and Pimples: A Comparative Table
| Feature | Acne | Pimples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A skin condition with various types of blemishes. | An inflamed bump on the skin. |
| Frequency & Spread | Multiple, recurring blemishes across larger areas. | Sporadic, isolated spots. |
| Duration | Long-term condition, can persist for years. | Resolves in days to weeks. |
| Depth | Involves deeper skin structures, like nodules or cysts. | Superficial, affecting outermost skin layers. |
| Causes | Hormones, bacteria, genetics, excessive oil production. | Clogged pores, bacteria, occasional hormonal changes. |
| Treatment | Comprehensive skincare, might need prescription treatments. | Managed with over-the-counter products. |
| Scarring Potential | Can lead to permanent scars if untreated or severe. | Rarely leaves scars unless picked or irritated. |
| Relation to Conditions | Acne is the broader condition. | Pimples are a symptom, not a condition on their own. |
Key Takeaways
- Acne is a skin disease that affects the hair follicles and oil glands, while pimples are one symptom of acne.
- Acne can cause different types of pimples on the skin, such as blackheads, whiteheads, or red bumps.
- Pimples are small infected bumps that can be pink or red in color and may have a white or yellowish head filled with pus.
- Both acne and pimples can be treated with creams, medications, and lifestyle changes.
Quick Overview of Acne and Pimples
1. Acne: Definition, Causes & Treatment
- Definition: Acne is a broader skin condition that can manifest in various forms, including blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and nodules. It’s a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin’s oil glands and hair follicles.
- Causes: Acne can be caused by multiple factors, including hormonal changes, genetics, excessive oil production, and certain bacteria on the skin.
- Treatment: Managing acne might require a combination of over-the-counter products, prescription medications, and sometimes even specialized treatments or procedures.
2. Pimples: Definition, Causes & Treatment
- Definition: Pimples are inflamed bumps on the skin filled with pus. They are essentially one of the manifestations or symptoms of acne.
- Causes: While anyone can get an occasional pimple due to various reasons like stress, diet, or hormonal fluctuations, it doesn’t necessarily indicate the presence of the acne condition.
- Treatment: Pimples can often be treated with topical treatments, which might resolve independently after a while.
While pimples are a common symptom of acne, their occasional appearance doesn’t automatically classify someone’s skin as acne-prone. Acne-prone skin is more consistently susceptible to breakouts and requires more specific care and management.
What is Acne?
Acne is a skin disease that affects the hair follicles and oil glands, while pimples are specific symptoms of acne in the form of infected bumps or pus-filled breakouts.
Acne as a skin disease
Acne is a skin disease that touches the hair follicles and oil glands. It can cause different types of pimples to show up on the skin. This happens when your hair follicles get full of oil and dead skin cells.
Your skin may have blackheads, whiteheads or red, tender bumps if you have acne. The main reason for acne is infected hair follicles in the skin. You can treat it with creams or medicine or by changing your life.
Pimples as a symptom of acne
Pimples are one of the symptoms of acne, which is a skin disease. Acne affects the hair follicles and oil glands in the skin. When these become infected, they can lead to the development of pimples.
Pimples are small growths that can be pink or slightly red in color. They may also become inflamed or discolored. Pimples are usually singular infected bumps on the skin’s surface, but acne can cause several pus-filled breakouts spread across the skin.
Fortunately, both acne and pimples can be treated with various methods, such as topical creams, medications, and lifestyle changes. Taking care of your skin through proper hygiene practices is important to prevent and manage acne and pimples effectively.
Causes and Symptoms of Acne
Various factors can contribute to the development of acne, such as hormonal changes, excessive oil production, clogged pores, and bacterial infections. Symptoms of acne include the presence of whiteheads, blackheads, inflamed papules or pustules on the skin.
Common causes of acne
Acne develops due to various factors, including:
- Overproduction of oil by the skin’s oil glands
- Blockage of hair follicles by dead skin cells and oil
- Bacterial infection in the plugged hair follicles
- Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty or menstrual cycles
- Certain medications or hormonal treatments that affect oil production
- Genetic predisposition to developing acne
- High levels of stress
- Poor skincare habits or using comedogenic products
Common symptoms of acne
Acne can cause different symptoms on the skin. These include:
- Red or pink bumps on the skin
- Pus-filled breakouts
- Inflamed and swollen areas
- Skin blemishes such as whiteheads and blackheads
- Clogged pores
- Pain or tenderness in affected areas
- Scarring or dark spots after the acne clears up
What are Pimples?
Pimples are caused by hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria buildup, and clogged pores. Symptoms of pimples include redness, swelling, tenderness, and the formation of pus-filled breakouts on the skin.
Causes and Symptoms of Pimples
Factors leading to pimple formation
Pimples are formed when certain factors cause the skin’s hair follicles and oil glands to become clogged. These factors include:
- Excess oil production: When the sebaceous glands produce too much oil, it can mix with dead skin cells and block the hair follicles, leading to pimple formation.
- Bacterial growth: Bacteria on the skin, specifically Propionibacterium acnes, can contribute to inflammation and pimple development.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty or hormonal imbalances, can increase oil production and lead to more frequent pimples.
- Clogged pores: When the openings of the hair follicles become blocked by a combination of oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, it can result in the formation of pimples.
- Irritation or friction: Rubbing or touching the skin excessively can irritate the hair follicles and trigger pimple formation.
Identifying the symptoms of pimples
- Pimples are small growths that appear on the surface of the skin.
- They can be pink or slightly red in color.
- Pimples are often raised and can feel tender or painful to touch.
- Some pimples may have a white or yellowish head, indicating the presence of pus.
- Pimples can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, chest, and back.
- They may be accompanied by other acne symptoms such as blackheads, whiteheads, or clogged pores.
The scientific term for a pimple is “comedo” (plural: comedones). A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. There are two main types of comedones:
- Open comedo (blackhead): This is a clogged pore that remains open at the skin’s surface, allowing the trapped sebum, bacteria, and dead skin cells to oxidize and turn black.
- Closed comedo (whitehead): This is a clogged pore that is closed at the surface, trapping the sebum, bacteria, and dead skin cells underneath, giving it a white appearance.
Depending on the depth and severity of the inflammation, both types can develop into larger, inflamed forms of pimples, such as papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, acne is a skin condition affecting hair follicles and oil glands. On the other hand, pimples are one of the symptoms of acne. While pimples are small infected bumps that can be pink or red in color, acne can cause various types of breakouts on the skin.
By understanding their differences and seeking proper treatment, it is possible to manage and prevent both acne and pimples for healthier-looking skin.
FAQs
Q: What is the Difference Between Acne and Pimples?
A: Acne is a condition that causes inflammation of the skin’s follicle and is characterized by the presence of different types of acne such as cystic acne and non-comedogenic acne. Pimples, on the other hand, are one of the many types of acne and are caused by the buildup of sebum in the skin’s follicle, which causes a pimple to form on the skin’s surface.
Q: How can I prevent acne?
A: Acne prevention can be achieved by following a few simple steps. It’s a good idea to rinse your face with a gentle cleanser twice a day and avoid using harsh scrubs or exfoliants that can irritate the skin. Additionally, using non-comedogenic moisturizers and avoiding oily products can help prevent acne. If you have persistent acne, it’s always best to see a dermatologist who can prescribe topical retinoids or other prescription medications to treat your acne effectively.
Q: Why does acne form?
A: Acne is formed when the skin’s follicle, which is connected to an oil gland that produces sebum, becomes clogged. This clog can be caused by a variety of factors including excess sebum production, dead skin cells, and bacteria. The clogged follicle causes inflammation, leading to the formation of acne.
Q: What is the role of sebum in acne formation?
A: Sebum is an oily substance produced by the skin’s oil glands. It plays a crucial role in developing acne, as excessive sebum production can lead to clogged follicles. When the follicles become clogged, it creates an environment where bacteria can thrive and cause inflammation, resulting in the formation of acne.
Q: When should I see a dermatologist for my acne?
A: If you have tried over-the-counter treatments and haven’t seen improvement in your acne or if your acne is severe and causing significant distress, it is recommended to see a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a skincare expert who can prescribe topical medications, such as tretinoin or adapalene, to treat acne effectively.
Q: How can I help prevent acne breakouts?
A: In addition to using proper skincare products, you can make a few lifestyle changes to help prevent acne breakouts. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding certain triggers like chocolate is important, which is thought to exacerbate acne in some individuals. Also, touching or picking at your face can introduce bacteria and worsen your acne, so avoiding this habit is best.
Q: What are some common treatments for acne?
A: There are several common treatments for acne, depending on the severity and type of acne. Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin or adapalene, are often prescribed by dermatologists as they help to unclog follicles and promote skin cell turnover. Other treatments may include prescription topical medications, oral medications, or laser or light therapies in severe cases.
Q: How often should I apply acne medication?
A: The frequency of applying acne medication can vary depending on the specific product and its strength. Generally, it’s recommended to apply acne medication once or twice daily. However, it’s important to follow the instructions provided by your dermatologist or the product label to ensure proper usage.
Q: Can using too many skincare products make my acne worse?
A: Using too many skincare products, especially ones that are not suitable for your skin type or are too harsh, can irritate your skin and worsen your acne. It’s important to find a balance and use products that are gentle and non-comedogenic. Consulting with a dermatologist can help you determine the best skincare routine for your specific needs.
Q: How does laser treatment help with acne?
A: Laser treatment for acne is a non-invasive procedure that targets the bacteria, oil glands, and inflammation associated with acne. It works by killing the bacteria that cause acne and reducing sebum production. Laser treatment can also help to improve the appearance of acne scars. However, it’s important to consult an experienced dermatologist to determine if laser treatment suits your specific condition.
References
- Dréno B, Araviiskaia E, Kerob D, Andriessen A, Anfilova M, Arenbergerova M, et al. Nonprescription acne vulgaris treatments: Their role in our treatment armamentarium—An international panel discussion. J Cosmet Dermatol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Aug 11]; 19(9):2201–11. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.13497.
- Ayer J, Burrows N. Acne: more than skin deep. Postgrad Med J [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2023 Aug 11]; 82(970):500–6. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2585707/.
- Kraft J, Freiman A. Management of acne. CMAJ [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2023 Aug 11]; 183(7):E430–5. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3080563/.
- Chovatiya R. Acne Treatment. JAMA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Aug 11]; 326(20):2087. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.16599.

